What Is Ultraviolet Radiation?
Ultraviolet Radiation
Utraviolet radiation is all around us. In the image above you can imagine all of those uv rays beaming straight into our eyes.
Quickly we slip on our sunglasses to protect our eyes.
We are surrounded by radiation of all kinds including visible light and radiation we can not see like ultraviolet radiation, radio signals, x-rays and more.
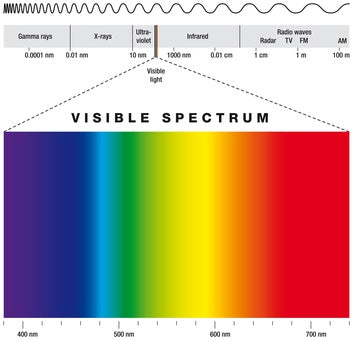
We measure radiation in wavelengths and radio waves are longer while gamma rays are much shorter.
The unit of measure we use to describe wavelengths is nano meters (nm).
Visible light rays are in the 700nm to 400nm range while ultraviolet radiation is in the 400nm to 190nm range.
As the wavelengths shorten they become more dangerous.
This is why it is important to always wear a good pair of aviator sunglasses when outdoors.
What Is Ultraviolet Radiation?
We see visible light with our naked eyes but we can not see UV radiation with our naked eye. Visible light has all of the colors in the rainbow in it.
Ultraviolet radiation wavelengths start just beyond the violet wavelength end of the rainbow. UV radiation has a wavelength just the same as visible light, radar and radio signals do.
Wavelength refers to the frequency while amplitude refers to the strength or intensity of the wave. Different wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation will have different effects on people.
For example, we use x-rays in cancer therapy to kill cancerous cells while infrared light rays keep us warm.
The ABCs of Ultraviolet Radiation

First of all those UV rays nearest the visible light spectrum have a wavelength of 400nm to 320nm and are called UV-A radiation. UV-A radiation is one of the causes of cataracts in our eyes.
The next shorter UV rays have a wavelength of 320nm to 290nm and is called UV-B radiation. In addition UV-B radiation is responsible for both skin and eye burns.
The shortest UV rays have a wavelength of 290nm to 190nm and are called UV-C radiation. UV-C radiation is much stronger and causes more severe skin and eye burns as well as skin cancer.
This can damage your exposed skin and in particular can happen around your eye sockets.
Where Does Ultraviolet Radiation Come From?

Our Sun is the greatest source of ultraviolet radiation by far; however, there are many man-made sources of ultraviolet radiation as well.
Ultraviolet radiation does serve some useful purposes in our lives. Ultraviolet radiation is used in industrial processes for curing inks and resins.
It is also used in medical processes like phototherapy as well as in dental processes to kill bacteria. Most of us understand that uv radiation is used in sun tanning booths.
However, ultraviolet radiation can also be very harmful to humans by causing injury or disease in eyes and skin.
Health Effects Of UV Radiation
Some exposure to ultraviolet radiation is good for us.
For example, ultraviolet radiation stimulates Vitamin D production in our bodies and UV lamps can used for treating diseases like psoriasis or jaundice in newborn babies.
In addition, UV lamps can be used by those who want that lovely summer tan in the dead of winter. However, excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation sometimes causes skin cancer, sunburn, accelerated skin aging or cataracts in your eyes along with other eye diseases and injuries.
The degree of risk depends on the ultraviolet wavelength, the intensity of uv rays and the length of time you are exposed to ultraviolet radiation. Ultraviolet light (UV radiation) is the most common cause of radiation injury to the eye.
While the cornea absorbs most of the UV radiation the damage to the corneal epithelium is cumulative, similar to the effects of sunburn.
Unprotected exposure of the eyes to the sun or exposure to sun on highly reflective surfaces like snow fields can lead to direct cornea injury and damage.
UV Radiation Effects On Eyes
Our eyes are particularly sensitive to the effects of uv radiation. For example, even a very short exposure of our eyes to ultraviolet radiation can cause painful (but normally temporary) conditions. Some of those conditions are conjunctivitus or photokeratitis. These are painful conditions because they inflame the cornea of the eye causing your eyes to water and blurry vision. Another disorder caused by exposure to UV rays is "flash burn", "ground-glass eye ball" and "snow blindness". Add to that the fact that red sore eyes after a long day in bright sunlight can make us tired and ornery. Our eyes are most sensitive to ultraviolet radiation that is in the 210nm to 320nm range (also known as UV-C and UV-B) but the cornea is most susceptible to absorbing UV rays of 280nms. UV-A ultraviolet radiation can cause cataracts in our eyes.
Those Most At Risk From UV Radiation
Many humans are at risk from the potential harm uv radiation can cause them. This is an abbreviated list of some of the occupations where the danger from ultraviolet radiation is highest:Sunglasses Are Essential To Protect Your Eyes
An excellent pair of aviator sunglasses will absorb 98 to 100% of harmful uv radiation and are essential for anyone who spends a great deal of time outdoors. Whether you are outdoors for work or pleasure the UV rays from the sun are working on your skin and eyes. When you spend prolonged exposure to the sun those UV rays can cause problems for your skin and eyes. Always protect your eyes from harmful uv radiation by wearing a quality pair of sunglasses. Never buy those cheap sunglasses you find in the aisles of pharmacies, malls and mega grocery stores!Video On Ultraviolet Radiation
Aviator Sunglasses
On our website you can find a great selection of excellent sunglasses at Randolph Engineering Sunglasses. You will find a style to suit you and sunglasses which will protect your eyes from the harmful effects of ultraviolet radiation. Keep your eyes cool and protected today my friend! p.s. Please share "What Is Ultraviolet Radiation?" with your friends. Thanks!
p.s. Please share "What Is Ultraviolet Radiation?" with your friends. Thanks!


Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.